An Allegory of Peace and the Arts c. 1635-8
Oil on canvas, mounted on board | 479 cm (sight diameter) | RCIN 408464

Orazio Gentileschi (1563-1639) & Artemisia Gentileschi (1593-1652)
An Allegory of Peace and the Arts c. 1635-8

Orazio Gentileschi (1563-1639) & Artemisia Gentileschi (1593-1652)
An Allegory of Peace and the Arts c. 1635-8
Orazio Gentileschi (1563-1639) & Artemisia Gentileschi (1593-1652)
An Allegory of Peace and the Arts c. 1635-8

Orazio Gentileschi (1563-1639) & Artemisia Gentileschi (1593-1652)
An Allegory of Peace and the Arts c. 1635-8

Orazio Gentileschi (1563-1639) & Artemisia Gentileschi (1593-1652)
An Allegory of Peace and the Arts c. 1635-8






-
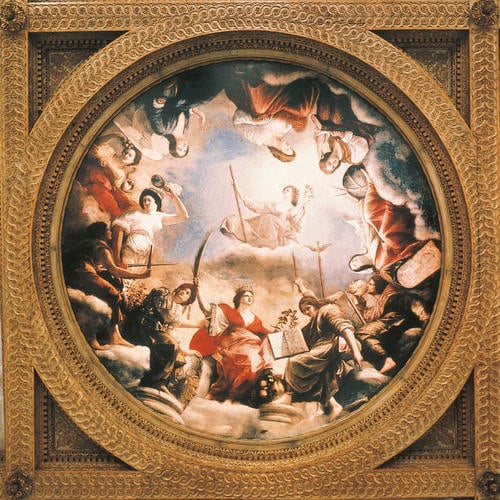
From about 1635 to 1638 the Florentine artist Orazio Gentileschi, helped by his daughter Artemisia, painted this ceiling for Queen Henrietta Maria for the Great Hall of the Queen’s House, Greenwich. The ceiling, made up of this central tondo flanked by eight other canvases, celebrates the reign of her husband King Charles I, for under his benign governance, Peace reigns and the liberal arts flourish. All twenty-six figures in the ceiling, apart from one, are female, embodying the power of women in a residence which was stamped with Henrietta Maria’s taste and patronage.
Artemisia may have assisted her ailing father, who died in February 1639. She probably arrived in London early in the summer of 1638, and if the ceiling was installed in the autumn of that year, she would have had time to paint some of muses and personifications of the arts in the outer canvases, for example the figures of Polyhymnia and Euterpe. Many of these figures have the dramatic chiaroscuro and more powerful physiques of Artemisia’s work compared to the refined and artificial style of her father’s paintings. Some have suggested she also painted figures in the central roundel.
It is hard to make conclusive decisions about Artemisia’s contribution to the ceiling because of its appearance today. Unfortunately the ceiling was reduced in size when it was transferred to Marlborough House early in the eighteenth century. The outer canvases were trimmed and space between figures reduced by cutting out sections resulting in a loss of perspective and distortions in scale. Incisions from the removal of sections are particularly evident in the sky. The ceiling has suffered substantial paint loss, probably caused by damp conditions and has had several campaigns of restoration, with much repainting. Figures in the lower section of the composition are much better preserved with rich colours, and a meticulous rendering of fabrics and details, such as the flowers and fruit of Victory’s cornucopia and the head of Medusa on Wisdom’s shield.
The architect and designer Inigo Jones, must have devised the iconography of the ceiling with Orazio. Cesare Ripa’s Iconologia, a popular hand book for allegorical personifications, was the principal source for the figures, although in some cases they do not precisely match the descriptions in Ripa, and cannot be identified with certainty.
High in the heavens at the centre is the personification of Peace, crowned with olive leaves with a staff in one hand and olive branch in the other. Below her is Victory or Glory, wearing a golden crown and holding a palm frond in one hand and laurel wreath in the other and resting her foot on a cornucopia of flowers and fruit. To the left of her is the armed figure of Wisdom/Reason/Strength. Her foot rests on a column, she points to Victory and steadies a shield decorated with the head of Medusa, the attribute of Wisdom or Minerva. She looks towards the Trivium of the Liberal Arts, just as Minerva, the patron of arts and sciences, traditionally introduces us to the Liberal Arts. The first of the Trivium is Grammar, the correct use of language, who sharpens the sword of Rhetoric with her rasp, while watering flourishing plants with her left hand. Rhetoric, the science of expressions and persuasion, is striking all in white with plumed helmet, and holds a sword in one hand and a mirror to Grammar in the other. Logic/Dialectics, who helps one arrive at the truth, holds a snake in one hand and a posy of flowers in the other.
To the right of Victory/Glory is the first of the Quadrivium, the four liberal arts related to mathematics and science. Astrology, like Wisdom/Reason/Strength, points to Victory with her right hand, which also props open a book of stars resting on her knee. She too rests a foot on the base of a column. Behind her is the winged staff or caduceus of Mercury the mediator between gods and mortals. Arithmetic rests a tablet with numbers on her knee. Music, here concerned with the ratio and proportion of music, holds up a wind instrument. Geometry, representing the calculation of spaces, has dividers and banded globe in one hand and a tablet with planimetric figures in the other.
The remaining figures are more difficult to identify: Meditation, resting her head on her left hand, a closed book on her lap; Agriculture, one of the Mechanical Arts, (or Concord, or Abundance), wearing a garland of corn and a sheaf on her lap; and the winged figure of Religion or Love of God, one hand raised to heaven, the other resting on a globe.
In the long panels around the central scene are the nine Muses, each has a sphere of influence over poetic inspiration and the creative arts.
In the corners are roundels with the personifications of the arts: Sculpture (with a carved head) and Architecture (using dividers to measure a hexagram on a tablet). Painting, (creating the figure of Minerva on a panel) and Music, represented by the god Apollo, holding a viola da braccio. He was the patron of poetry and music and the leader of the nine Muses.
Under the reign of Peace every art and science works in harmony to guide the extraordinary achievements of mankind. Viewers seeing the ceiling in its original pristine state would have been transported to an ethereal world filled with light and heavenly figures, all painted in rich colours with such clarity and delicacy. We can appreciate these qualities today in this impressive last work by Orazio Gentileschi assisted by his daughter Artemisia.
Provenance
Commissioned by Queen Henrietta Maria to decorate the ceiling of the Great Hall at the Queen's House, Greenwich
-
Creator(s)
-
Medium and techniques
Oil on canvas, mounted on board
Measurements
479 cm (sight diameter)
548.6 cm (Height) (sight diameter)
Other number(s)
ML add-Gentileschi








